The question of how to propagate the gooseberry, arises in many gardeners. With the observance of technology, the shoots and gooseberry cuttings are easily rooted. This process is not complicated, even a novice can. Therefore, to grow healthy gooseberry bushes is not difficult.
Table of contents
Methods of reproduction of gooseberry in autumn and summer
There are several ways to reproduce gooseberry. The choice depends on how much seedlings need to be obtained, the age of the uterine bush, the growth of annual and two-year shoots, their development.It is also important what breed is required to propagate - already existing on the site, or a new one growing in another garden.
Layering
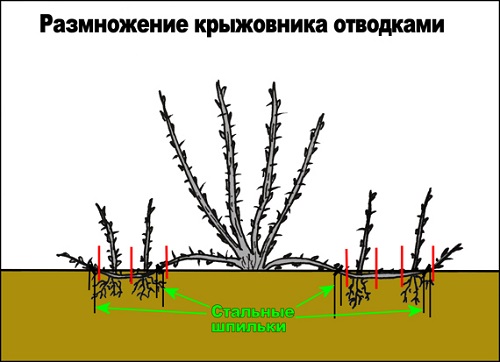
Gooseberries are propagated by horizontal, arcuate or vertical layering. This method is effective because along the entire length of the shoot, near the buds, there are root buds. With constant humidity, they are easily awakened and start to grow.
The desired age of uterine gooseberries from 3 to 5 years.
The soil around the bush must be prepared in advance. Her weed, dug to a depth of 10 cm, make humus or rotted manure, mixed with the upper layer of soil and level.
Horizontal layouts give a large number of shoots. With such reproduction, the fruiting of the gooseberry does not stop.
Strongly developed annual and biennial shoots are suitable for cutting. Older branches can also be used, but there will be fewer seedlings. To wake up the kidneys, the top must be pinched.
Breeding technology:
- perpendicular to the base of the bush, they make grooves 3 cm deep;
- the selected shoot is placed on the bottom, slightly pressing into the ground;
- fixed in several places with long metal brackets or wooden slingshots;
- the ground must be constantly wet;
- after the buds awaken, and new shoots grow by 15 cm, they are spud up to a height of about 5 cm;
- when the increase will increase by another 15 cm, they are re-hilling. The total height of the land mound should not be higher than 10 cm above the soil level.
It is necessary to keep the soil moist, in the hot summer the ground around the bush is mulched.
In the fall or spring of next year, the shoot is carefully digged, the grown shoots are separated, leaving a small part of the parent branch on each one.
Sort:
- seedlings, whose roots are underdeveloped, rejected;
- with weak roots planted for rearing on a separate garden bed;
- with a strong growth of the roots planted in a permanent place.
Arc-shaped cuttings are used in the event that it is necessary to obtain 2-3 strongly developed bushes.
The difference of this method from reproduction by horizontal layers is that only one seedling is obtained from one shoot, with a developed root system and lateral branches.This makes it possible to transplant it immediately to a permanent place, and the crop is received in the second year after transplantation.
Shoots root in the spring and summer, in the fall they are separated from the parent plant. You can root shoots of the current year. They are pinned in June, and deposited next spring.
Technology:
- dig a hole 10 cm deep;
- the branch is gently bent and placed in the hole so that the bud near which the roots will grow is in the middle of the hole;
- secure with a bracket;
- fall asleep fertile land, forming a mound of about 10 cm;
- above the ground should remain the end of the branch, a height of 35-40 cm;
- set the peg, I tie up the shoot so that it is upright;
- pinch the top to strengthen the branching.
In September, the escape is cut off from the mother bush, but transplanted only in early October.
Vertical layering propagated gooseberry over 4-5 years. Simultaneously with the reproduction of the bush rejuvenates.Gooseberry will not bear fruit in the current and next year.
Technology:
- small, underdeveloped shoots cut out completely;
- the remaining branches are cut to a height of 20 cm, this stimulates the growth of shoots from the lower buds;
- when the shoots grow by 25 cm, and their base is slightly woody, hilling of young shoots to a height of 5 cm is performed;
- after three weeks, they pile up again, increasing the height of the knoll by 5 cm.
Falling asleep bushes, you should make sure that new shoots remain at some distance from each other. This is necessary so that the roots are intertwined as little as possible, and not damaged during transplantation.
In autumn, the ground is carefully otbrebayut, separate the resulting seedlings and transplanted to a permanent place.
You may also be interested in the following articles about gooseberries:
Cuttings
This method allows you to get a lot of planting material. It is practiced when there is a need to diversify the varieties of gooseberries in the garden, or if the species you like grows in another area.
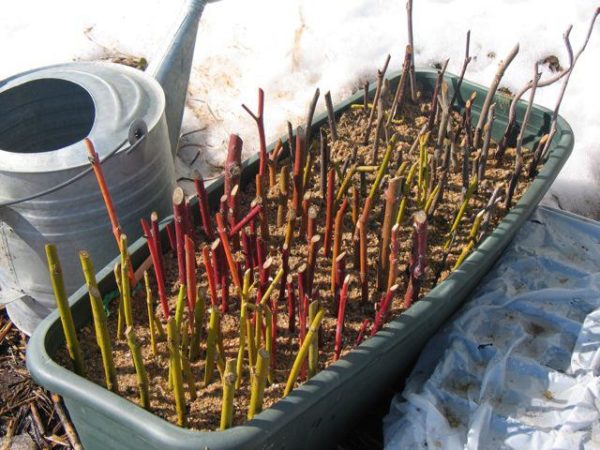
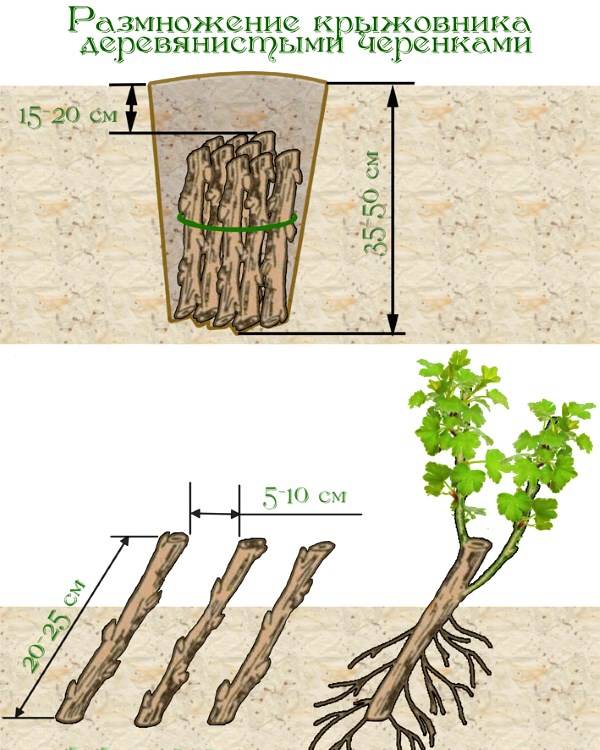
Lignified cuttings are prepared using shoots growing from the base of the bush. You can cut the top of the branches.
A shrub should not be older than 8-10 years, because cuttings cut from an old shrub root poorly. The bush must be healthy, not damaged by pests.
The event is held in early autumn.
Part of the stem for grafting should be 15-20 cm long, and have at least 4 buds. Under the bottom make a cut at a slight angle, retreating 1 cm. The distance from the upper bud to the cut should also be 1 cm. Cut straight.

Technology:
- prepare the bed in advance, making it compost;
- cuttings are planted so that only one upper kidney remains above the ground;
- planting is carried out by stitching, the distance between the seedlings is 15 cm;
- have cuttings at a slight slope;
- for the winter they are warmed with leaf litter or agrofibre.
Subsequent care is to maintain soil moisture, weeding and loosening. By the fall, one shoot grows, next spring it is cut, leaving two buds.
The permanent place is transplanted in the autumn, in the second year after grafting.
Green or combined (half-lignified) cuttings rooted in the greenhouse. Young lateral growths on the lower part of the branch are suitable for this. TOCombined cuttings root better than green ones, but in order to obtain a large number of seedlings, it is recommended to cut shoots of a different type.
The best time for breeding is the first half of summer. On each handle should be two sheets. The lower cut make a diagonal.
Technology:
- the ends of the cuttings are dipped into the solution of any stimulator of root formation and kept for as long as indicated in the instructions;
- greenhouse with nutrient soil must be prepared in advance;
- disembarkation is carried out according to the scheme 6x6 cm;
- deepen the stalk to 1 cm;
- Cover with glass or cellophane.
The temperature in the greenhouse should be maintained at 23-25 °, the soil should not dry out.Best rooting takes place at high humidity. It is necessary to spray the seedlings in hot weather several times a day. To control the temperature, a thermometer is placed inside the greenhouse. As soon as it rises, carry out airing.
Attention should be paid to the lighting. The greenhouse is placed in a place where the diffused light falls. You can shade the planting by pulling white agrofibre with a density of 15g per meter over them2sticking leafy branches from any tree from the sunny side, or having covered the glass with whitewash.
When shoots begin to grow, they are hardened daily. After 3-4 weeks shelter removed. In the autumn, pinching is carried out, and it is warmed for winter. In early spring, until the buds have blossomed, they are transplanted to a permanent place, transferring the seedling with a lump of earth.
By branches
This method is used for propagation of overgrown gooseberries over the age of 5 years. Choose a strong branch with several branches, growing from the edge of the bush.
It is necessary to separate it with part of the root system. To do this, the ground is raked to bare the roots. If at the base of the selected branch roots are weak, it is not suitable for transplantation, you should choose another one.
Sharp narrow shovels cut off part of the bush, and cut them from the bottom to a depth of 25 cm. Carefully transfer them to a new place, trying to keep as much soil as possible on the roots.
Gooseberries are watered and spud up to a height of 25 cm. The hole formed at the site of the dug seedling is covered with earth.

Dividing bush
Most often, the division of the bush is carried out in two cases:
- gooseberry has grown old, growing in one place for more than 10 years, in connection with this, the yield has decreased and its quality has deteriorated;
- It is required to transplant the gooseberry to another place.
The method is effective, carried out at the beginning or end of the growing season.
Technology:
- a bush is dug out and the ground is washed from the roots with water from a hose;
- determine the place of separation of rhizomes. There should be two or three shoots and a healthy part of the roots on one deal;
- division is carried out with a sharp knife, separated by hands. A very old bush is chopped up with an ax.
- delenki with old branches, with underdeveloped roots are rejected;
- transplanted immediately to a permanent place;
- landing spud;
- branches shortened by 1/3.

Cuttings
A lignified annual or biennial sprout will be required. It leaves 5 buds. The upper cut is made straight, not higher than 1 cm above the kidney. For the lower cut, 1.5 cm recede from the kidney, cut obliquely.
Escape planted obliquely, deepening three buds, and two are left for the development of young shoots. Hilling is not carried out.
If the annual increase was 15-20 cm, then the next year they put him in a permanent place with a clod of earth.
The best time to breed shrubs
When to multiply gooseberries - depends on the method chosen.
Reproduction by layings is carried out in the early spring when the earth warms up. It is important to do this before the beginning of the growing season.
Autumn is suitable for rooting lignified cuttings, and green ones are planted in the greenhouse all of June and in the beginning of July. Branch cutting is carried out in the same period.
The division of a bush or the separation from it of a perennial branch is carried out before the buds swell, or after the end of leaf fall.
Quality seedlings can only be obtained from a healthy, developed bush. The plant must be prepared in advance: cut out all the sick and weak branches, feed, carry out preventive treatment of diseases and pests.Next season the gooseberry will be ready and able to multiply correctly and quickly.
