When breeding poultry farmers are inevitably faced with diseases that are prone to birds. The incidence of livestock is not a pleasant one, because, first of all, this is a high level of economic damage, plus all diseases spent on bird breeding can be nullified by the disease. Marek's disease is one of the fairly widespread ailments.which may be particularly prone to chickens, broilers, as well as other types of domestic birds. How to recognize the disease, as well as how to deal with it, is described in this article.
Table of contents
Marek's disease
The disease was first described by a researcher from Hungary by the name of Marek in 1907. Despite the fact that Marek himself dubbed the disease of chicken polyneuritis, in the future the name of the disease was associated with the name of the discoverer. In our country, for the first time they started talking about Marek's disease in 1930, at the same time its study began. There are three forms of the disease:
- Neuralin which the peripheral nervous system is affected. In severe cases, accompanied by paresis and paralysis in diseased individuals.
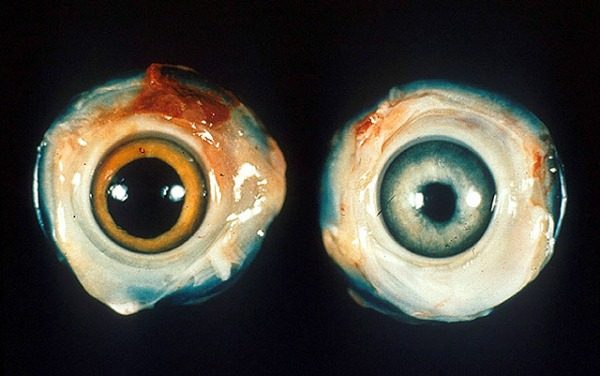
- Ocular, eye, in other words. Accompanied by deterioration of vision, and in some cases, its loss. The lethal outcome reaches 30%.
- Visceral, with the formation of tumors on the internal organs, built of solid tissue.

By the type of course the disease is classified into two forms:
- Sharp
- Classic
Symptoms and signs in chickens and adults
The incubation period ranges from two weeks to 150 days.largely depends on the age of the bird, genetic predisposition,individual resistance of the individual system to the immune system. Depending on the form of the course, the symptoms of the disease differ.

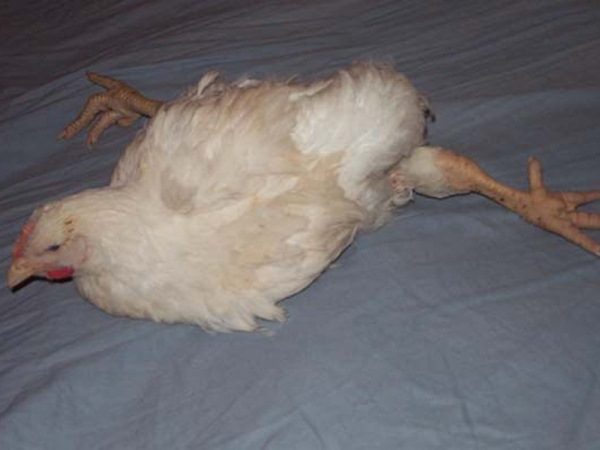
In the acute form of Marek's disease, symptoms similar to leukemia are observed. The young are subject to the disease, chickens aged from 30 days to five months. Due to the high virulence within 7-14 days, the whole herd is exposed to the disease. Some individuals suffer from paresis and paralysis. The main symptoms include digestive disorders, weight loss, loss of appetite, impotence. Clinical signs are due to the formation of tumors on parenchymal organs, leading to disruptions in the body. Accompanied by a sharp decline in productivity and high mortality of livestock.
In the classical form of the course, mortality does not exceed 30%.. Most often affects the nervous system, at least - the eyes. When depression of the nervous system may occur, lameness, sagging of the wings and tail, possibly folding the neck. Separate individuals are prone to semi-parachutes, which, as a rule, most often pass without a trace. In case the infection affects the organs of vision,there is a color change in the iris, often accompanied by visual impairment, and in some cases complete blindness. The pupil itself changes, taking a narrow, pear-shaped or other shape, with no reaction to the light. With the defeat of the eyes, the sick individuals most often die within a period of one month to one and a half years.
Treatment of ailment
The disease is caused by the Herpes virus and is highly contagious. Members of the flock who have become asleep become the source of the spread of infection, releasing the virus into the external environment within 7–20 days from the moment of infection. The virus carrier lasts one and a half - two years, in some cases during the whole period of life. In the case of recovery, a strong immunity is formed with the ability to transfer antibodies to the progeny.
Currently, there is no specialized treatment for this ailment.. If an outbreak of infection is detected, antiviral therapy is carried out, quarantine measures are applied, and in most cases, slaughter is carried out to prevent spread.The only, most proven way to prevent the incidence - vaccines.
In adult chickens
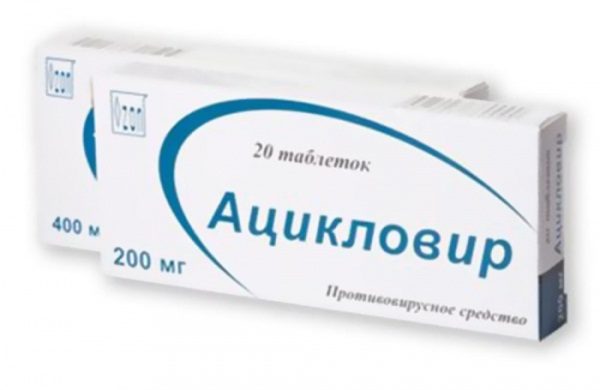
Perhaps only in the initial stages of the disease, when the bird has not yet been subjected to paralysis. For the purpose of antiviral therapy In the treatment most commonly used is the domestic drug Acyclovir.. However, even timely initiated therapy does not guarantee the prevention of the death of the bird.
U broilers
As a method for the treatment of meat breeding chickens prophylactic vaccinationwhich is done to the chicks at day old. In some cases, revaccination is performed at the age of 10-20 days. With a lesion of 5-10% of the total number, it is not advisable to treat adult beef breeds of chickens. After the slaughter of all infected livestock, the house should be thoroughly disinfected. before placing a new batch of young.
In geese, ducks and other birds
Herpes are highly susceptible to chickens, fewer than turkeys, quails, then aquatic birds such as geese, ducks and swans. The only successful form of treatment is preventing illness through immunization.
Vaccination
Inoculate the bird with live attenuated viruses. Immunization of young stock is carried out at day old. After the procedure, the birds produce anti-bodies to the virus. The following vaccines are used for immunization:
- Liquid virus vaccine based on strains of chicken herpes virus.
- Liquid virus vaccine based on turkey herpes virus strains.
- Vaccine Nobilis Rismavac and Nobilis / SA
Measures to combat the spread of the virus
To prevent an increase in the incidence in the room where the affected individuals were kept, thorough disinfection according to veterinary standards is carried out. Incubation of eggs is possible after four-time treatment with formaldehyde vapors. Resuming the breeding of agricultural birds is allowed not earlier than one month after the measures related to the cleaning of the territory from the virus. Despite the fact that the virus itself quickly dies in the environment, it is able to preserve virulence in feather follicles for 8 months.
In order for the breeding of agricultural poultry to remain profitable, and the birds themselves were not exposed to viruses and pathogens, special attention must be paid to the purchase of young stock and the preparation of the house.
Buy hatching eggs, chickens, adult chickens and other species of birds should be only from trusted breeders. Particular emphasis should be placed on the preparation of the room, which will continue to contain living creatures. Preventive sanation measuresspent in advance in the house, reduce the possibility of infection of young animals at times.

I finally realized that with our bird. After reading this article, I saw how they can and should be treated! Now I can advise friends to read!
Elena, advise, but remember that it is better to consult a veterinarian.
Hello, I faced a problem than I did not treat (((chickens both simple and broilers grow poorly, lag behind in growth and weight gain, some emaciated, weakened die, 2% sit on the splits or refuse legs, there was a case of head unscrewing, wheezing and an increase in temperature. We can assume that this is this virus?
Angelina, it’s best to consult a veterinarian.