Growing tomatoes in the greenhouse allows plants to be protected from frost, drying out of the soil and adverse weather conditions. However, diseases can overtake tomatoes in a greenhouse environment, and in case of a temperature violation or watering, on the contrary, it provokes the reproduction of harmful microorganisms and pests.
Table of contents
The main diseases of tomatoes in the greenhouse and methods of dealing with them
Why can diseases occur in the greenhouse and how to treat the seedlings so that the leaves do not curl? Spores can easily tolerate winter in plant debris or directly in the soil. The disease can also develop as a result of using for planting untested seeds that are already infected. Insects also contribute to the spread of disease.
Danger lurks young tomato shoots at each stage of growth, and in the case of tomatoes, the situation is complicated by the rapid onset of the flowering period, when the use of chemicals is no longer recommended. It is impossible to sit with folded arms, after planting seedlings in a polycarbonate greenhouse, it is necessary to plan preventive measures using traditional methods. Among the most famous and simple tools:
- wood ash;
- dolomite flour;
- crushed quicklime
- Onion peel helps with fungi and late blight
- Crushed quicklime
- Wood ash
- Garlic against fungus
- Dolomite flour
To prevent disease fit the usual products that are in each kitchen:
- milk (against phytophthora);
- garlic (from fungal infections);
- salt (from phytophtora);
- onion peel (from fungus and phytophthora).
Why are leaves curling or late blight tomato?
The most common disease of tomatoes caused by the development of fungus. Fungal spores awaken at high humidity. If good air circulation is available in the open ground, it is very difficult to avoid dampness in the greenhouse and a disease environment is created. In addition, a concomitant factor of the disease is the temperature difference, which is typical for the spring period, when the difference between the night and day index is over 10-15 degrees.
Symptoms of the disease:
- dark brown and brown spots on the leaves;
- stained fruit;
- drying and twisting foliage.
As a preventive measure, it is appropriate to equip the greenhouse with a drip irrigation system. You can do the simplest invention of plastic bottles. Cutting off their bottom, you need to set the capacity of the neck into the ground near the root zone (towards the roots). Conducting irrigation in this way, the evaporation of moisture is practically eliminated, and hence the moisture level is easier to maintain at the desired level.
- Phytophthora on tomato leaves
- Fruit Phytophthora
- Fitosporin - an effective remedy against phytophthora
In addition to traditional methods, special preparations are used:
- Barrier;
- Phytosporin;
- Barrier.
Brown leaf spot
Disease characteristic of greenhouse plants. You can recognize it by the yellow round growing spots, which are formed initially on the lower leaves of tomatoes. On the reverse side of the affected foliage there is a brown velvety plaque (mushroom spores).
A little later, the greens dry up and curl, and after some time the plant dries out. Often the disease manifests itself during flowering and fruiting. With high humidity up to 95% and low light brown spot occurs very intensively. At detection of primary symptoms it is recommended to immediately treat the plants with Bordeaux mixture or preparations Barrier, Barrier.
- Brown spot
- Mosaic on tomato leaves
- Tomato cracking
Mosaic
Viral disease, the danger of which is the lack of treatment. Therefore, it is important to pay special attention to prevention. The infected plant is recognized simply by the mosaic color, the leaves are covered with light and dark green spots, which are rapidly increasing, merging into large islands. When identifying the first signs it is recommended to remove the bush and dispose of it. It is desirable to decontaminate the landing site with a special solution.
Cracking fruit
Cracks on the fruits of tomatoes are often formed as a result of violations of the irrigation regime. But this is not the only reason. Exposure of nitrogen-containing fertilizers to the soil and improper use of pollination stimulants can provoke cracking. Before using any formulations for the garden, it is necessary to carefully study the instructions and not to violate the recommended dosage of the product.
White plaque or how to treat against rot?
Tomatoes grown in the greenhouse are prone to rot.The disease is of several types, which differ, first of all, in the plant's affected area.
- Gray rot
- Brown rot
- Root rot
- Vertex Rot
- Root rot develops mainly due to improper soil preparation in the greenhouse. This may be an excess of slightly swollen manure, too wet soil, poor drainage or lack of it.
- Vertex rot is recognized by characteristic spots on the fruit (the disease does not affect the tops). It provokes the formation of deformation and spotting of tomatoes, mainly a violation of agricultural engineering (improper watering, overdose of nitrogen fertilizers, etc.).
- Gray rot is recognized by brown wet spots on the stem and foliage. Ash-gray scurf indicates sporulation. The disease develops as a result of poor ventilation in the greenhouse with an increased level of humidity.
- Brown rot affects areas near the stem and fruits. On the surface of the tomato can be seen a small stain, but almost the entire core is rotten. Fresh manure is considered the main provoker of the disease, therefore it is not recommended as a fertilizer for the greenhouse.
As a preventive measure, regular spraying of the beds with infusion of garlic should be carried out, as well as powdered with wood ash.
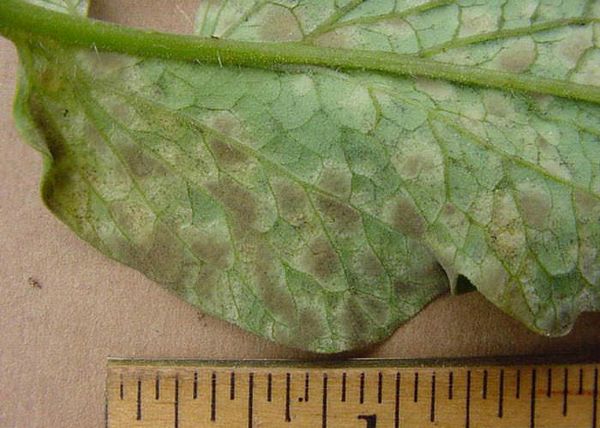
Leaf mold
To detect the first signs of the disease often succeeds in the flowering period. Light green spots appear on the upper side of the leaf, becoming yellowish-white in color. The affected leaves turn yellow at first, dry up, coagulate, and then die off.

Control measures:
- greenhouse disinfection;
- replacement of soil (remove the layer at least 30 cm);
- adjustment of air humidity in the greenhouse by regular ventilation;
- seed dressing;
- spraying the bed when the first signs are detected with a suspension of zineb or other preparations.
Macroscopic
Dry spotting can be easily identified by elongated spots of brown color on the leaves, stem, cuttings, stem. Fruits are covered with depressed brown spots. The main provocateur of the disease is high humidity and poor airing. At low temperatures, the intensity of the development of macroporosis increases.

If a large part of the bush is covered with spots, it makes no sense to save it. The faster the fungal spores are removed, the less likely the spread of fungal infection to healthy plants.
Of the drugs effectively use Bordeaux mixture.
Prevention of tomato diseases in the greenhouse
Many inexperienced gardeners are concerned about the question, what measures should be taken to prevent diseases from affecting tomatoes? An effective protective base is built on prevention, which includes:
- observance of the rules of crop rotation (it is impossible to plant a single crop in one place every year, predecessors are also carefully selected);
- autumn digging area (preferably before the frost, so that the larvae and spores are frozen out);
- careful cleaning of the garden at the end of the season (plant residues become a winter haven for harmful microorganisms);
- soil disinfection before planting;
- disinfection of greenhouse surfaces at the end of the season and in the spring;
- replacement of the soil layer (performed periodically to update the land or after diseases);
- treatment of plants with preparations of biological origin (Bayleton, Aktellik, Farmaid-3, etc.).

Due to greenhouse cultivation, harvesting can begin several weeks earlier than when growing tomatoes in open ground. There are no difficulties in the technology, you just need to follow the generally accepted rules. Then you can eat plenty of tomatoes in the summer and make preparations for the winter.