Potatoes are very popular among even the most sophisticated gourmets. And although it is a simple vegetable, which is not uncommon, it also cannot always please the summer residents, as it is attacked by diseases that can significantly reduce crop yields.
Table of contents
The most common diseases of potatoes and methods of dealing with them.
And then we will talk about the most common diseases and pests that they love to profit from potatoes and how to quickly and easily get rid of them.
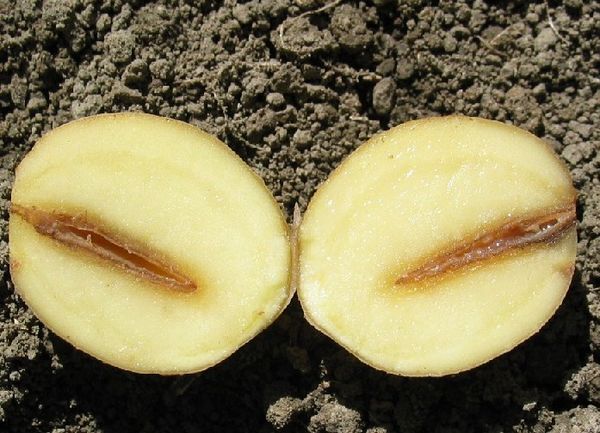
Late blight
Its appearance is caused by lower fungi, such as oomycetes. If microorganisms are present in the soil, then the probability of infection with this disease is very high.

In addition, these mushrooms are very fond of moisture, because summer rain and a temperature of more than 15 degrees is great to help their spread.
Detecting signs of late blight is not at all difficult, because the leaves begin to turn black, and from below you can see white spores on them, which indicate the presence of fungi.
The difficulty is that wind and rainwater can easily spread these disputes on the field. Tubers blacken and carry a greater threat to neighboring bushes.
To avoid infection, you must adhere to the following precautions:
- potatoes should be planted in the same place no more than 3 years in a row;
- landing is better to make on the plain, as well as in a sunny and well-ventilated place;
- follows keep the distance between the bushes;
- do not plant seeds already affected;
- before planting, potatoes must be thoroughly dried in fresh air with a temperature of 18 degrees for 2 weeks;
- that tubers were resistant to the disease, they are treated Immunocytophyte or Agat-25K.
- Immunocytophyte
- Agat-25K
Common Scab
Potatoes also suffer from 3 types of scab: black, powdery and silver.
Black scab
As it is also called rozoktonioz, can give summer residents a lot of trouble. The disease affects tubers and tops.
Excellent conditions for the development of black scab are high humidity and air temperature not lower than 18 degrees.
How to get rid of rozoktonioza, you will be prompted by the following tips:
- do not plant infected tubers into the ground;
- Do not sow in the same place for several years in a row.
- if the soil is hit by a black scab, then process planting material Prestige or Maxim.
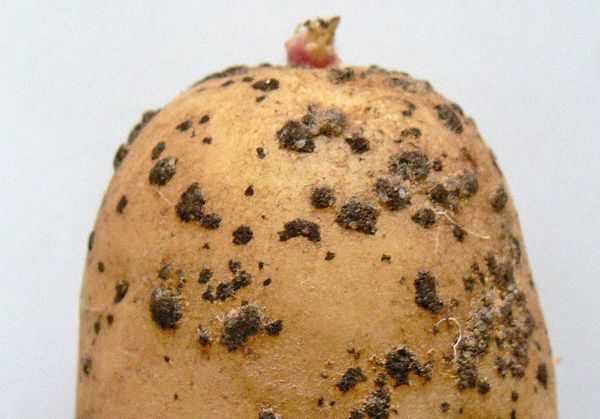

Powdery
Also affects the leaves and tubers. On the potato, you can see red ulcers, which eventually destroy the plant. The disease is transmitted by air or through humus or chicken droppings.
To combat this disease apply a special solution, for the preparation of which they take:
- 10 liters of water;
- 3% bleach;
- 5% of copper sulfate.
For watering use 300 ml per bush.
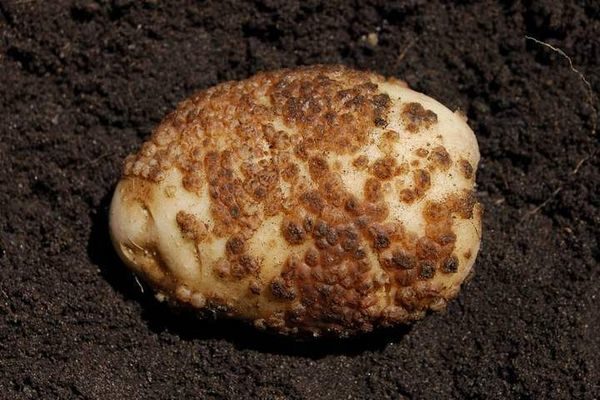

Silvery
Insidious disease that can dry the stem or the tuber itself. It manifests itself in the form of silver spots, which can cover almost 50% of the surface.
The disease, which is suitable temperature not less than 3 degrees of heat and humidity of at least 80%. And disputes live in tubers for a very long time, because they easily tolerate even cold.
In the fight against this disease will help such means as:
- Maksimthey are treated with tubers 3 days before planting and dried well in the sun.
- Kvadriswhich is applied to the plant immediately before planting.
- Silver scab
- Maksim
- Kvadris
- Prestige
L virus
Symptoms of the disease depend on the variety and growing conditions. Often it can be wrinkled, spots or dying off the foliage.
To kill a virus you need:
- do not use infected tubers as a planting material;
- to wage a continuous struggle with aphids and cicadas, in which such means as Aktara and Karate Zeon.
- Aktara
- Karate zeon
Wireworm
The wireworm - the larva of the click beetle delivers no less trouble to the gardeners. The beetle in April carries out its flight and lays eggs into the soil, therefore there is no such place that it would not be affected by it. However, be sure to control its population, otherwise it can lead to disastrous results.
Potato-stricken potatoes cannot be stored for long, because he will quickly begin to rot.
The favorite habitat for the wireworm is the wheatgrass rhizome, dense thickets and acidic soil.
To reduce the population of these beetles, the following rules should be followed:
- it is necessary to change the landing site every 3 years;
- in the spring and autumn it is necessary to dig up the ground to kill the larvae;
- do not leave tops and tubers for the winter on the site, as they will help the wireworms and the larvae to move the winter well;
- It should be planted in the garden plants that perfectly repel these beetles. These include marigolds, which emit a hated smell for wireworm and legumes, in the rhizomes of which there are bacteria, that emit terrible nitrogen for the beetle.
- You can use the popular method. To do this, 100 g of celandine insist 3 days in 10 liters of water, and then water the bushes.

Also get rid of the wireworm will help and all sorts of bait:
- On 1 m2 should dig a jar, at the bottom of which put the cut potatoes. Beetles will definitely fall into it. Just do not forget to check the jars and destroy the beetles every 3 days, as well as change the bait.
- You can also bury the tuber in the ground and set a stick for marking and repeat the above procedure every 3 days.
- In the spring on the site you can put cellophane and lubricate it with sugar solution. Beetles will surely flock to the scent and stick to the trap.
Nematode
This worm is able to catch up with real horror on the gardeners, because it is almost invulnerable:
- he does not care for either high or low temperatures;
- he is easy endures drought and flood.
- even a lethal dose of radiation for a person is powerless against this worm.
In addition, the parasite can multiply very quickly.
To get rid of nematodes will take decades, and the population can be reduced in 2 years.
In the fight against nematode apply the following measures:
- They declare quarantine and do not export potatoes outside the region.
- Do not plant this culture in the same place more than 3 years in a row.
- After 2 years, it is desirable to change the planting material.
- Soil treated with urea.
- Tubers before planting watered with a solution of potassium permanganate, the calculation of 0.5 g per 10 liters of water.
Altenaria
Symptoms are clearly visible 20 days before flowering, when the leaves cover with brown spots. Spots are also visible on tubers as a result of damage.
To prevent disease, tubers are treated with drugs such as Integral or Agat-25. Young shoots moistened with Bravo.
- Alternaria potato
- Bravo
Blackleg
Black leg is another disease that has clearly expressed symptoms. With such a lesion:
- leaves turn yellow, curl and dry;
- roots and tops first turn black and then rot;
- they are easy to wrest from the soil.
If the disease progresses rapidly before or during flowering, then tubers will not be formed.
A favorable condition for the black leg is a rainy summer. The carriers of this disease are the Colorado beetles, aphids and cicadas.
To combat the black leg should adhere to such precautions:
- do not use infected tubers and land for planting;
- diseased bushes rip out and burn, or buried in 1 meter, sprinkling bleach.
- harvesting is carried out in dry weather;
- before storing the crop in the basement, it is well dried;
- storage is treated with 3% lime solution;
- also helps the processing of potatoes before planting Maxim or Fitosporin.
- Blackleg
- Phytosporin
Potato cancer
This disease, which causes the fungus, in the place where it penetrates into the plant, a growth is formed.
Transferred disease very easy:
- rainwater;
- with man's shoes;
- various insects;
- if the animal eats the affected plant, then it goes along with the manure and continues its livelihoods.
For the extermination of fungi of this species it is necessary:
- constantly change the place of planting culture;
- grow cancerous varieties: Early yellow, Smachny, Spark and many others;
- tubers are treated with a 1% suspension of foundationol.
- Potato cancer
- Fundazole
Potato pests
The most common pests that do not mind to eat potatoes, include:
- Colorado potato beetle;
- potato moth;
- Medvedka.
Colorado beetle
Actively destroys the stem, because of what tubers cannot develop normally. It multiplies rapidly, for 1 season born from 2 to 3 generations of Colorado beetles, who rush to fill his belly.

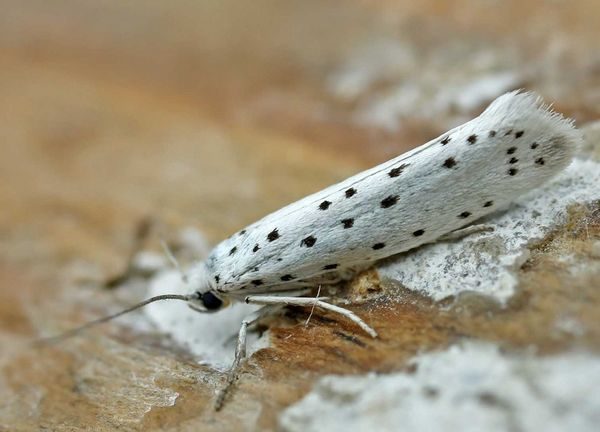
Potato moth
Cute white butterfly. Over time, it turns into a caterpillar and gnaws almost the entire tuber under the skin itself and leaves its excrement.
Also she can settle in the plant stem. For the emergence of a new generation takes only a month.
To reduce the number of tracks it is necessary:
- 2 weeks before harvesting, mow the tops;
- use a tool like 10% carboros. 90 g of this product are dissolved in 10 l of water.

Medvedka
It is not so easy to find her herself, since she lives underground, but it is also possible to outwit her.
You can also water the places of its distribution. 10% karbofos, 50 g diluted in 10 liters of water.
Potato Rot Types
No less dangerous is a disease called rot. There are several types of rot:
- ring;
- brown bacterial;
- mixed internal;
- wet
- dry.
Very often there are cases when ring and brown rot are confused. Although they are caused by different types of bacteria, but still on the leaves appear similar brown-yellow spots. However, if you squeeze the vessels, then a light yellow mass will appear when the ring rot appears, and when the brown rot is browned, the ring turns brown.
Ring
Does not live in the soil, she transferred to the next crop through seeds. Also, if folded tubers are stored next to healthy ones in storage, bacteria will penetrate through scratches or damaged peel.
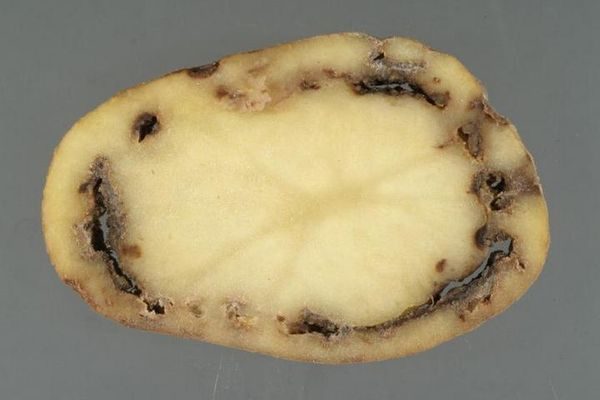
Brown
Can lay low in the soil and wait in the wings to get into the damaged tubers.
Mixed internal
In order to avoid the appearance of all the above types of rot, first of all it follows:
- change planting material regularly;
- change the landing site;
- after harvesting burn the tops;
- prevent mechanical damage to potatoes.
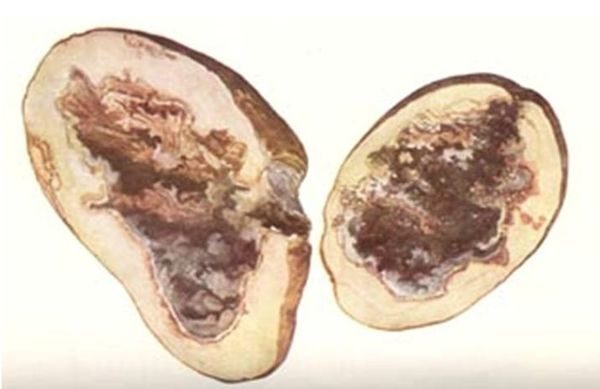
Wet
Can completely destroy the entire tuber in 15 days. Manifested this disease during storage. Most often, at the site of mechanical damage, the surface becomes soft and begins to rot.
Chemically overcome wet rot is impossible. In order not to expose potatoes to this disease should:
- put well-dried tubers in the storage;
- process the cellar with copper sulphate or lime;
- prevent mechanical damage and freezing of tubers.
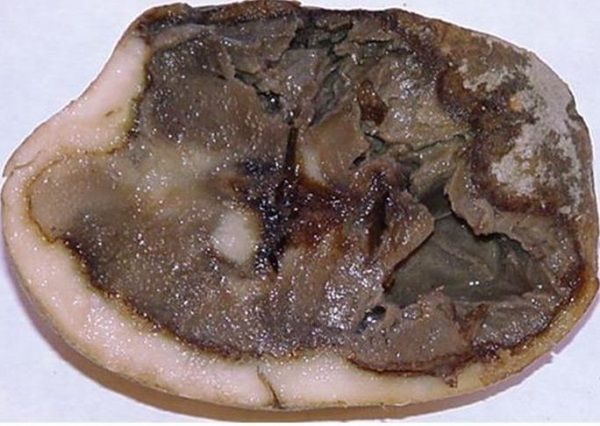
Dry
Bushes affected by this disease fade, slow down or disappear altogether.
To avoid its occurrence it is necessary:
- do not abuse fertilizers, as they emit a favorite nitrogen of this rot;
- remove the tops from the garden;
- change the place of landing and planting material.
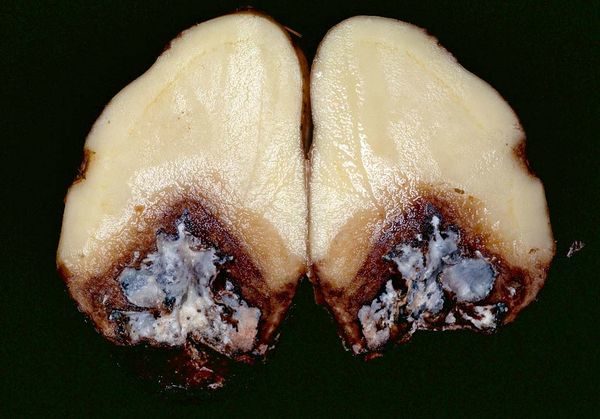
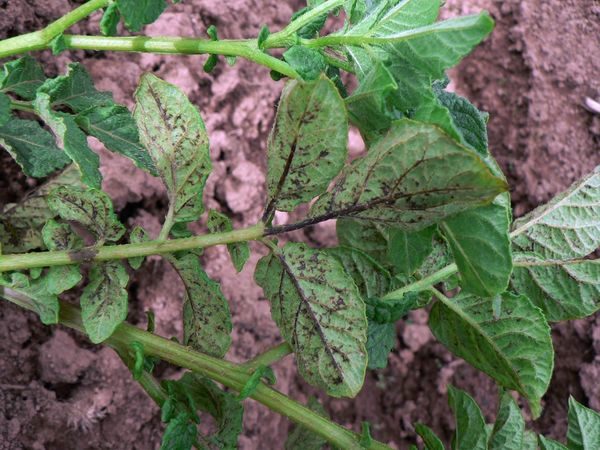
Potato mosaic
Mosaic is no less unpleasant disease that is caused by viruses. There are 2 ways to transmit this disease:
- various insects;
- If you treat an infected plant with a tool, and then apply it to a healthy one, then infection cannot be avoided.
Particular attention should be paid to the wrinkled and banded mosaic.
Wrinkled
Received its name according to the signs of the disease. The leaves begin to frown and curl inward. In addition, diseased cells cannot retain moisture, which is why the most a small drought causes the plant to die.
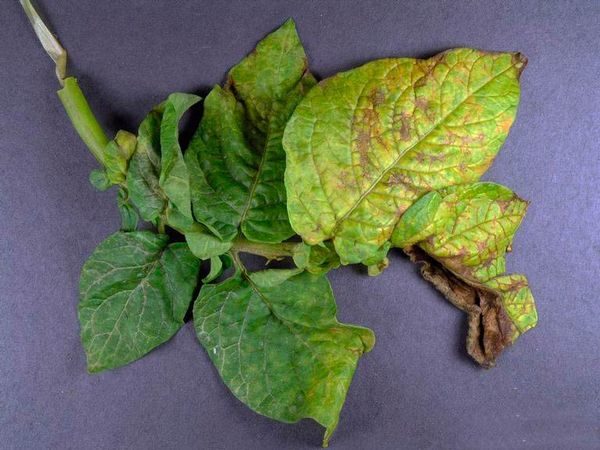

Banded Mosaic Virus
More aggressive and can destroy about 90% of the crop. At first strips appear on the vessels of the leaves, then the leaves die off, and there are only a few things left on the whole bush. As a result, the tuber generally ceases to grow.
To combat the mosaic also has its own methods:
- the virus of this disease dies at 60 degrees;
- infected tubers should not be planted, but easy to see with ultra light;
- germinated tubers should also be selected, since the sprouts of infected tubers will be weak;
- Before planting seeds should be treated with insecticides.

Potato diseases: classification
All diseases of potato are divided into the following groups:
- when stored;
- viral;
- mushroom;
- bacterial;
- non-infectious.
Table 1. The division of the disease of potatoes by type.
| Type of disease | Disease |
|
viral |
all types of mosaic leaf folding ciliary top curly dwarfism column wilting |
|
fungal |
Late blight fusarium dry rot black scab |
|
bacterial |
ring rot blackleg wet bacterial rot common scab mixed internal rot |
| non-infectious |
darkening of the pulp gray spot or melanosis tuber strangulation thermal damage to tubers freezing of tubers glandular spotting hollowness and deformation of tubers red or blue color of tuber pulp peel skin |
All these diseases can develop both during the ripening period of the potato and during storage.
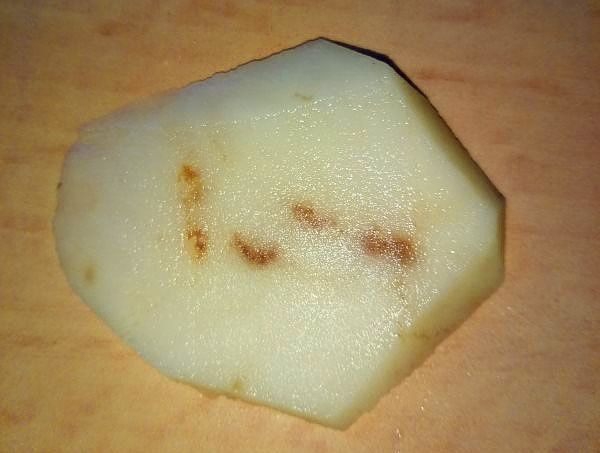
Why are there brown spots on potatoes
The cause of these spots are:
- low humidity;
- heat;
- lack of phosphorus.
Develops this disease only during growth, when storing potatoes, it freezes.
To prevent this disease from affecting your potatoes, you must apply nitrogen fertilizers, chill, and water the potatoes.

Insecticides
Today, there are many insecticides that will save your potatoes from diseases and all sorts of pests. The most effective of them include the following tools:
- Maksim - protects from a variety of diseases, and especially from all sorts of scab and fittovoroza.
- Kvadris - a tool that not only protects against many diseases, but also improves the growth of potatoes.
- Kruiser - excellent protection of tubers from various pests.
- Celeste Top - protects tops and tubers from pests, as well as from fungal diseases.
- Aktara - will protect potatoes for 60 days.
- Force - aims to destroy wireworms.
- Prestige - protects late varieties from rot, scab and Colorado beetles.
And also it should be noted such drugs as Imidor, Commander and Taboo.
- Potato Cruiser
- Celeste Top
- Imidor
As you can see, whatever disease or pests do not try to destroy your crop, yet they will not succeed if you competently care for your favorite potatoes. Therefore, in time fight against diseases and pests and you will achieve amazing results. Have a good harvest!