Potatoes firmly entered into the diet of our food. But contenders for eating potatoes exist besides us. And if you do not follow and do not care for the plant in the process of growth, then the harvest can not wait. Pests that eat the plant from the root to the flowers, a great many. Illustrations will help determine who eats the leaves or can nibble the crop tubers.
Table of contents
Colorado beetle
The beetle beetle is one of the most important pests not only of potatoes, but also of eggplant, physalis, tomato and sweet pepper.
One female beetle per season produces up to 700 seb pests. In the southern regions, two to three generations of the Colorado potato beetle hatch over the season. From eggs laid by the female, after one two weeks the larvae appear, which eat the flesh of the leaves on the tops of the plant.
After the larvae grow up a little, they crawl all over the plant and even into neighboring plants. After a couple of weeks of intense eating, they are buried in the soil to a depth of 10 centimeters for pupation. After three weeks, an adult pest crawls out of the ground in order to eat its offspring to produce its offspring.

In summer and autumn, in good dry weather, they are able to fly to other areas tens of kilometers at speeds of up to 8 kilometers per hour. The life of this beetle beetle lasts from one to three years.
Wireworm
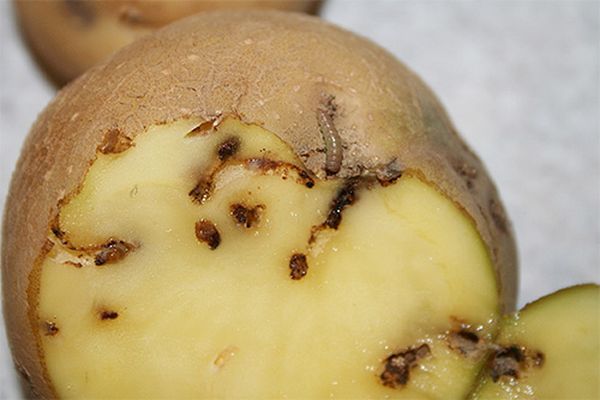
The wireworm is a larva of the beetle beetle. In the image of the larvae this species of beetle is from two to five years. And even in adulthood, he buries himself in the ground for the wintering up to 10 centimeters in depth. And in the state of the larvae, the nutcracker can be located underground at a depth of up to 60 centimeters.
Wireworm damages young shoots and tubers potatoes It bites, leaving behind it holes in which rot settles. Some types of wireworm damage not only potatoes, but also buds and young shoots of grapes.
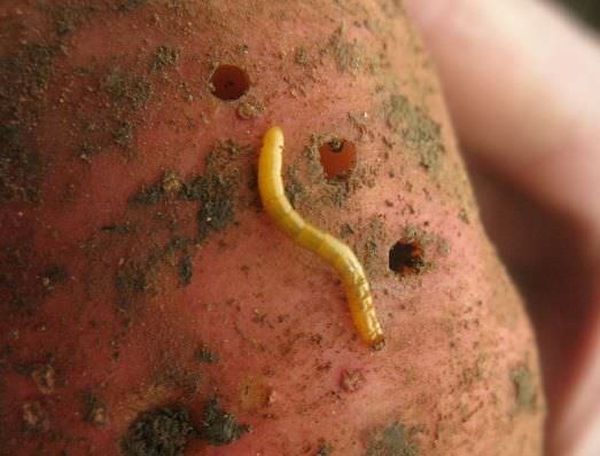
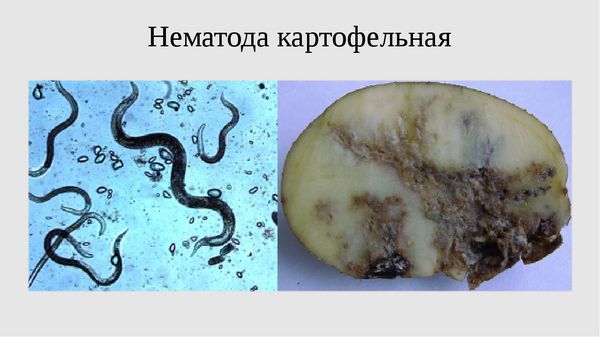
Nematodes
Today, more than 24,000 nematode species have been studied. They are parasitic roundworms. There are also free-living species.
Vegetation nematodes damage the root system very many plants. No exception and potatoes. The result of the activity of the nematode can be seen on the edges of the tubers in the form of soft parts of dark color.
Medvedki
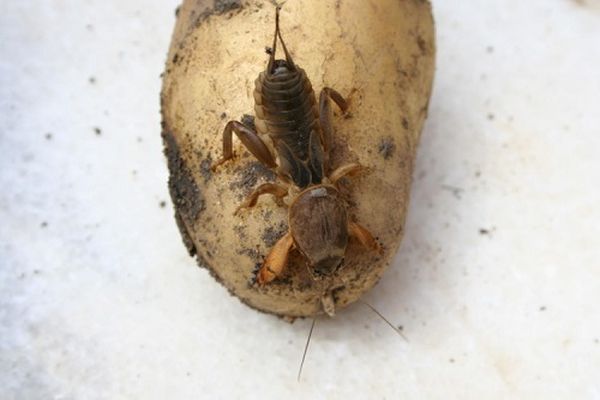
This is one of the major representatives of the family of burrowing insects. Medvedka belongs to the order Orthoptera. The length of this insect reaches 8 centimeters. Able to take off to a height of up to five meters.
They live in burrows, which they themselves dig. About 500 eggs are laid in a nest to a depth of 15 centimeters, which is made in warm soil, such as a compost heap. The size of the nest basically corresponds to the size of the individual.
Medvedka eats all that is underground: roots and bulbs of plants, potato tubers.

Caterpillars scoops
Potato scoop is the enemy of so many plant cultures. This is a butterfly whose caterpillars intensively eat such plants as potatoes, tomato, garlic, raspberries, lilies, strawberries, corn, toffee, rhubarb, onions, hops, beets, cabbage, cucumbers. It belongs to the scoop family.
Their caterpillars feed on stems, leaves and rhizomes. Do it at night, justifying its name.
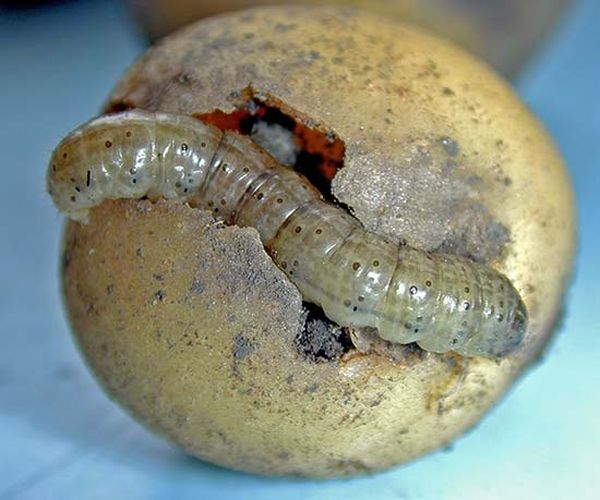
Potato moth
The life of this butterfly is only a couple of weeks, and during this time it lays up to 200 eggs, of which caterpillars appear in a week.
These caterpillars from 10 days to a month damage all parts of the potato plant. After this time, they turn into a pupa, and after another week again into a butterfly. To stop this endless cycle, at least on the scale of our land, our task is with you.

Cicadas
They belong to the family of semi-coleoptera jumping insects of small (from 1 to 3 centimeters) size.
They live during the day in anthills, and at night they go out to drink the juice of a plant under the protection of ants, making holes in the plant with their piercing-sucking mouth. Rot and pathogens penetrate into these holes with corresponding consequences.
Cicadas tolerate phytoplasma and viral diseases plants. Parts of the damaged plants, after the work of the cycling, wither and die.

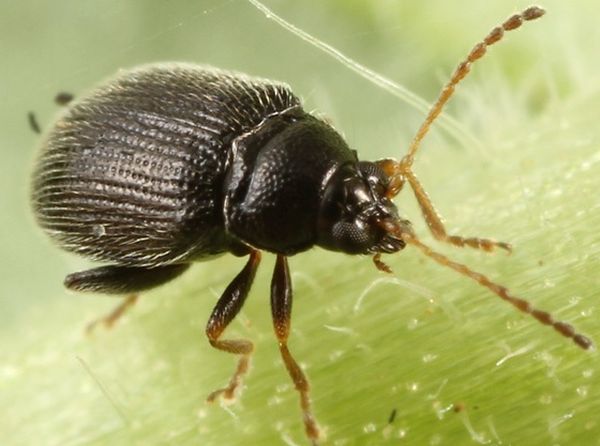
Potato flea
A small bug up to three millimeters in size, which in adulthood eats the upper part of a potato plant, this is a potato flea.
The larvae of this beetle feed the lower part of the plant and its root system. Potato flea is very active in dry weather.

Pest control in potatoes and in the ground
Ways to combat pests are quite diverse. But they can be divided into chemical, mechanical and folk.
Mechanical methods of fighting insects
The mechanical method of controlling pests of potatoes include:
- autumn and spring digging land before and after planting potatoes
- pest collection by hands.
Digging up the soil in late autumn, you can remove the bear's nest outside. Winter cold will surely destroy the whole laying of the bear. Besides digging, there is a chance to once again dig the very Medvedka.
Loosening, hilling and removing weeds also helps to get rid of some pests. Loosening and hilling kills the pest larvae. Adult pests can live on weeds.
When collecting pests by hand, do not forget that the Colorado potato beetle can pretend to be dead. Therefore, be sure to destroy the collected insects so as to be sure of it.

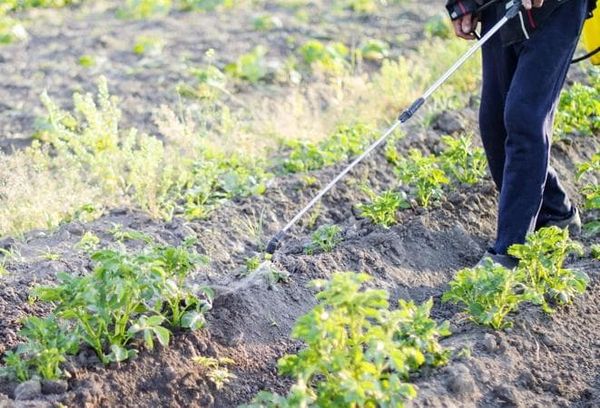
Chemical
This method implies chemical processing.
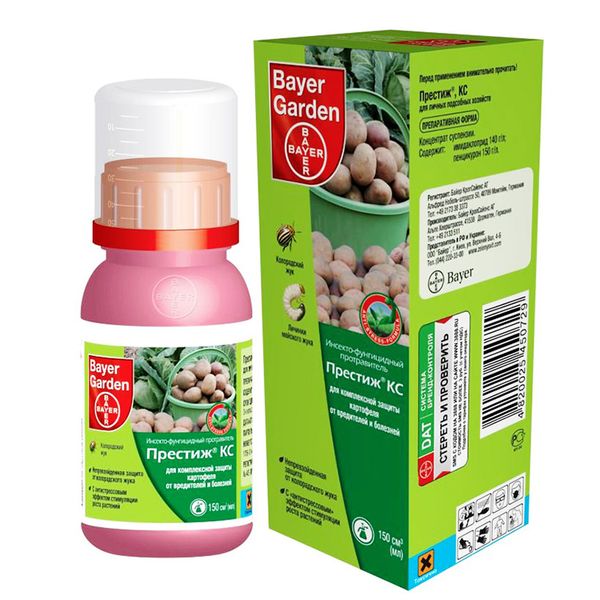
The most popular drug today is Prestige. Also use the analogue of this drug Taboo. They are either sprayed planting a couple of weeks before planting, or watered into the hole directly during planting potatoes.
These drugs “pickle” the seed, helping to get rid of pests and prevent certain types of diseases.

Folk remedies
On their home plots folk remedies can quite effectively deal with unwanted insects.
Very often, before planting, seed potatoes are treated with either manganese solutionor diluted with water ash. Just put the ash in the hole before planting. The procedure helps to repel insects and prevents the development of harmful larvae in the ground.
In order to prevent the emergence of wireworms, in addition to ash in the ground, you need to add lime powder. For catching medvedki set beer bottles and traps. For catching the Colorado potato beetle "on the live bait" in early spring lay sliced potatoes.
In order to correctly and purposefully use methods of insect control, it is necessary to correctly determine the pest and what kind of harmful action it performs.

What are the gastronomic preferences of potato pests?
| Insects that eat the leaves of potatoes. | Colorado potato beetle, cicadas, potato flea |
| Insects eating the stalks of the plant. | Colorado potato beetle, Potato flea, Medvedka, Potato scoop, Potato moth |
| Pests that damage the roots and tubers of potatoes. | Colorado potato beetle, Wireworm, Potato flea, Nematode, Medvedka, Potato scoop |
There are so many ways to combat potato pests. But the best way to fight it prevent their occurrence.
Timely digging the garden, loosening the soil, processing the beds from weeds, constantly changing the potato planting site, pre-processing the seed and taking care of the plant during the growing season will help avoid not only problems with potato pests, but also prevent many plant diseases.
