The body of the domestic rabbit does not tolerate diseases, especially if they are caused by exposure to the virus. As a result, just yesterday, a completely healthy animal dies for no apparent reason. therefore The state of the rabbits must be monitored constantly., in time to notice the symptoms of the disease and isolate it from relatives, and also to do everything possible to cure it. In this article we will look at common diseases that cause rabbits to die, why they appear and what to do in such cases.
Table of contents
Why do rabbits die: causes of death
A common cause of disease and subsequent death of rabbits is violation of sanitary standards in the content. Untimely cleaning of cages, watering with dirty or spoiled water, all this adversely affects the health of the population. Especially badly affected by unbalanced diet, which further weakens the animal's immunity.
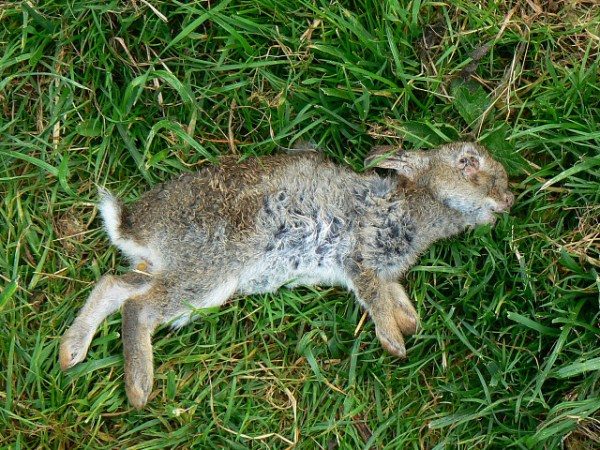

Rabbits die and have an attentive host, who provides their wards with good feeding, timely cleaning and disinfection of cells. The reason for this is viral and infectious diseaseswhich are common in the summer, because they are transferred not only from a sick animal to a healthy one, but also through insect bites.
The most common diseases of adults and young
- VGBK;
- myxomatosis;
- pasteurellosis;
- coccidosis;
- flatulence.
UHD (fever) - viral hemorrhagic disease of rabbits, when to do vaccination
The abbreviation stands for - rabbit viral hemorrhagic disease. This disease causes the death of rabbits. Disease prone animals from two months. VGBK or simple words fever, very contagious, it is transmitted not only through wool, meat and feces of infected individuals, but also by air. Mortality occurs in 90% of cases. It is not always possible to notice that the animal is infected, since UGBC may be asymptomatic. In the acute form, rabbits completely refuse to eat, behave restlessly, very quickly lose their strength and become slow-moving, but at the same time they convulsively pull their paws and throw back their heads.

The animal is experiencing pain, therefore, periodically publishes a squeak, possible blood discharge through the nose. Death occurs from 24 to 72 hours after infection. The disease affects and destroys the liver of the animal, and also causes pulmonary edema, which often becomes the cause of death, because the body has enough oxygen.
In order to protect your livestock, you need to use a special a vaccine that is given to baby rabbits at 45 days of age. Adults can be introduced at any time.The validity of the vaccine is one year, after which it is necessary to carry out revaccination. Treatment of the disease has not yet been developed, and the reasons for the recovery of individual individuals have not been established.
Myxomatosis (distemper), visible symptoms
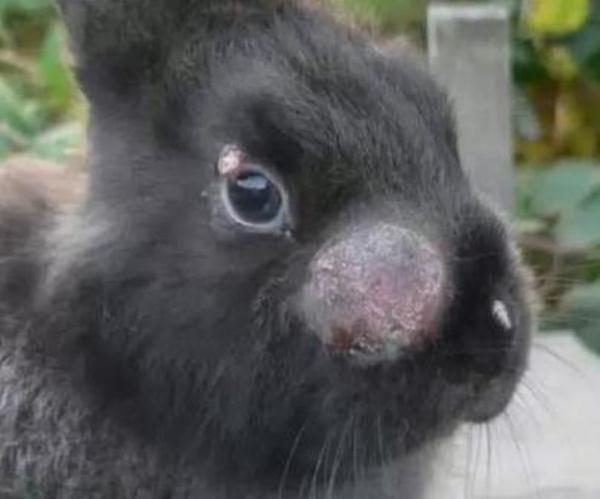
Disease transmitted through insect bites and causes profuse mucus secretion from the nose and eyes. An infected animal can live for a long time with these symptoms while infecting its relatives. Myxomatosis, in common chumka, very dangerous for young stock, in which mortality occurs much faster than in adults.
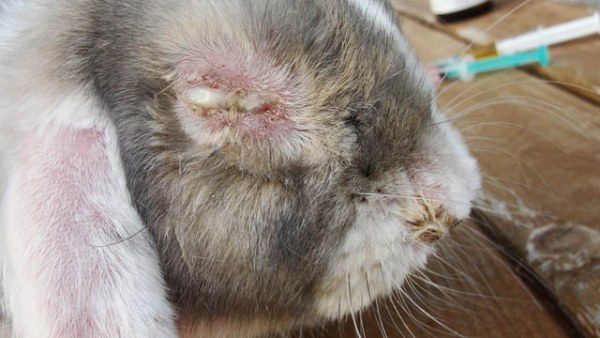
In addition to secreting mucus, infected individuals have swelling or nodular swelling in the nose, ears and eyes.
After the onset of symptoms, the disease rapidly develops and leads to the death of adult animals in about 10-14, and the young in 7 days.
Myxomatosis spreads very quickly, and if one infected rabbit is found on the farm, then most likely the others are already infected too. The disease does not have an effective treatment.therefore, vaccination is necessary for its prevention.The possible use of an associated vaccine, which has in its structure a strain of myxomatosis and UHDB, which eliminates the need to prick an animal with a syringe twice.
Pasteurellosis
Infectious disease capable of causing a massive death of livestock in just 2 days. The visible symptoms are runny nose, sneezing and lack of appetite. In contrast to the aforementioned diseases, which appeared relatively recently, pasteurellosis has been known for a very long time.
The disease is fatal., but on a much smaller scale than the first. Death occurs in 15-75% of cases. The better the feeding and sanitary conditions, the lower the percentage of death.
The disease can be acute or develop into a chronic one. In acute currents, the temperature of the animal rises to 41 degrees, after which shortness of breath, runny nose and sneezing begin. After several hours or days, such a rabbit most likely dies. In chronic form, the animal exhibits all the signs of rhinitis and conjunctivitis., making it difficult to timely diagnosis. The patient’s stool becomes liquid, there may be purulent abscesses under the skin, which open up after 1.5-2 months.Fortunately, this disease can be cured by resorting to drugs.
Coccidiosis
The disease is caused by parasitic protozoa of unicellular organisms. Parasites affect the liver and intestines. Each rabbit is a carrier coccidosisbut the clinical form is rare.
Coccidosis manifests itself clearly, which helps in its diagnosis. So sick animal has swollen belly and emaciated body, there is no appetite. The disease is transmitted by coccidian oocytes, which are present in the feed and water. Healthy animals with strong immunity can independently resist the development of coccidia to a painful clinical form.
During the slaughter of an infected rabbit, dotted light growths in the form of nodules are observed on the liver and in the intestines. In addition, the liver will increase 5 times. The disease is treated with antibiotics., but first of all it is necessary to improve the conditions of detention without allowing the accumulation of dirt and overcrowding of cells.
Flatulence
Flatulence or flatulence, a common cause of death. Since the rabbit's intestines are sensitive, if it fails, its work is difficult to restore and sometimes impossible. The cause of flatulence is a sharp change in the flora of the digestive system.. This can happen if the food was very wet or juicy, which was unusual for an animal.

With a flatulence rabbit falls into apathyHe suffers from colic and refuses to eat. This leads to fermentation in the intestines of food eaten, because it is not pushed new. As a consequence, bacteria develop in the digestive system, which begin to destroy the intestinal wall and lead to the death of the patient.
Other reasons for which livestock die
In addition to the common causes of the death of rabbits, there are several more rare, but also dangerous diseases.
Rabbits are prone to scabiesthat parasitize their ears. Ticks eats into the skin of the animal and drinks its blood, causing severe itching. Scabs appear in the ears, hair falls on them. The exhausted animal gradually fades, it refuses food, loses strength and dies after long torment. These parasites can be killed using modern drugs, so the rabbit can be cured.
Females during lactation are prone to infectious mastitis on the nipples. The cause of the disease are the wounds obtained from the sharp teeth of baby rabbits. These bites are natural, but if they are poorly maintained in a dirty cell, they begin to develop an infection that spreads throughout the body and infects the blood, resulting in a fatal outcome. Therefore, the cells with the rabbit feeding the young must be especially clean.
Causes of death of little rabbits
Rabbits at the age of up to a month are not susceptible to diseases, because they have strong immunity derived from mother's milk. But a strong immunity is not able to protect them from everything. Most frequent the reason for the death of little rabbits is the low temperature in the nest. They freeze to death even in hot summer, if they are not in a nest with litter and down of mother.
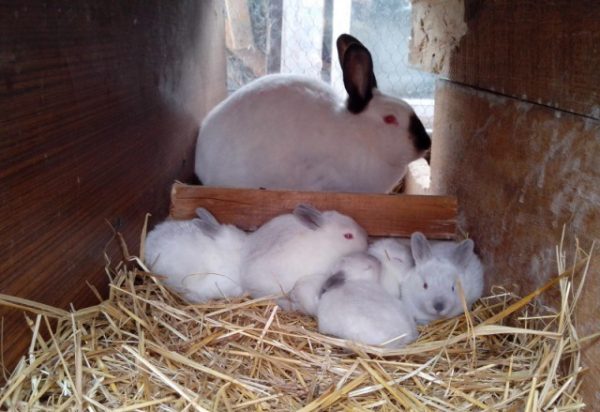

The next reason is hunger. Lack of mother's milk in the first days, It becomes an insurmountable obstacle for kids. Monitoring the milkiness of the female can be done by weighing baby rabbits. By measuring their total weight before and after feeding, you can determine how much milk they drank. In case of its lack, it is necessary to improve the feeding of the female, or to remove part of the offspring to another rabbit,which has children of the same age and who has no shortage of milk.
Treatment and prevention of diseases at home
Diseases like UHD and myxomatosis are not treated.and mortality among infected individuals is very high. At the same time they experience severe torment, so the animal is better to kill. The only panacea is vaccination, which is held every year.
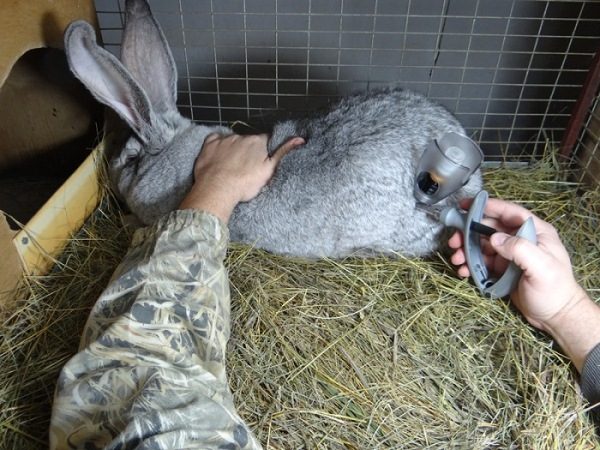

Pasteurellosis can be cured by using antibiotics and B vitamins, especially at the initial stage of the disease. Coccidiosis is eliminated under the influence of drugs:
- Trichopolus;
- Sulfadimezin;
- Khimkokkokd.
Thus, it is important to monitor the health of the rabbits, and periodically conduct a detailed inspection. Should not avoid vaccination at least against incurable diseases.. Good food and adherence to sanitary norms will preclude the development of most non-viral diseases
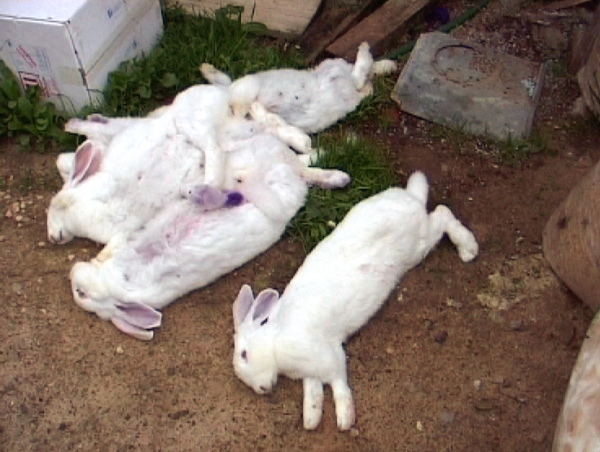

Unfortunately, rabbits very often die, sometimes for no apparent reason at all. My parents tried to breed rabbits, but refused this idea because of their high mortality.
I have been keeping rabbits for a very long time, and they are dying. It's a pity that three adults recently died. They opened pus in their urinary tissue. Tell me.
The trouble is ... 2 days ago, rabbits began to breathe for 2-3 months, there were no symptoms ... they just went to the cage, everyone is alive and healthy and after 5 minutes the bang is warm. Food did not change, the water supply is clean in the cells clean. P.S. No vaccine was pricked ... there were no such deaths in that year.
very similar to VGBK (hemorrhagic), last year all the livestock in 3 days was 100% dead. We relaxed and didn’t vaccinate, didn’t vaccinate for 4 years, everything was fine and now ... So, for no apparent reason, vigorous people ate and jumped, and in the evening one little garden with young and mother, the second and more. The last males died, but they didn’t wait any longer, they killed the remaining alive for meat. Now I vaccinate everyone, necessarily